Virtana’s Model Context Protocol Server
Traditional dashboards limit engagement in complex, AI-driven, multi-cloud infrastructure. To solve this issue, you can take advantage of the Virtana MCP Server: an extension of the Hybrid Observability platform with a native Model Context Protocol (MCP)-compatible server.
MCP Clients are chat-based interfaces that connect to remote MCP servers over streamable HTTP, so you can access data, perform actions, and receive responses through natural conversational queries without complex tooling. Together, the Virtana MCP Server and MCP Clients enable AI agents and assistants to retrieve alerts, entities, relationships, and metrics from Virtana-monitored environments, delivering clean, contextual, and human-friendly results.
Note
The examples in this guide were tested with the Goose client, which is an MCP-compatible chat client, and the OpenAI GPT 5.1 model. Goose connects to Virtana’s Alerts MCP server to provide real-time alert data through interactive, natural-language queries. However, you can use other compatible clients and models in your environment.
What is MCP
Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an open standard that enables AI agents to interact with external platforms and tools in a structured, consistent way.
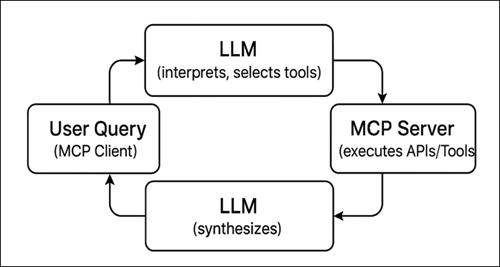
How MCP Works
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) enables AI agents to interact with external tools and data through a standardized client-server architecture over streamable HTTP. MCP acts as a secure bridge, allowing large language models (LLMs) to discover, call, and execute tools provided by MCP servers without custom integrations
Key Components
MCP Client: Client that sends the user’s natural language query to the LLM. Examples include Goose or other chat clients.
LLM: Large Language Model, such as OpenAI or Claude. LLMs interpret the query and decide which tools to call from the MCP server.
MCP Server: Server that hosts registered tools and APIs, executes tool calls based on LLM requests, and returns structured results.
APIs/Tools: The actual functions or endpoints exposed by the MCP server, such as Virtana Alerts API for real-time data.
Response Flow: FlowResults from the MCP server are sent back to LLM, which synthesizes a natural-language response sent to the client.
Generate OAuth credentials for the MCP client
You can generate OAuth client credentials by performing the following steps:
Navigate to Integrations in Settings and select Virtana Platform API.
In the Virtana Platform API page, click Generate OAuth Client Credentials.
The New Credentials window opens.
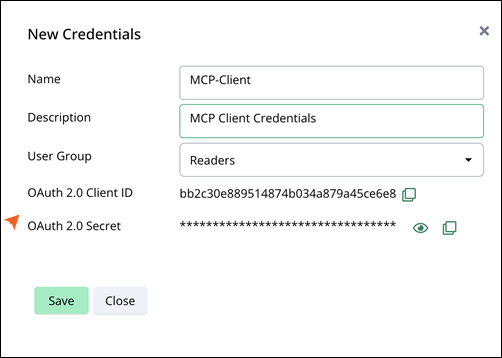
Enter the following details in the fields:
Name: MCP-Client
Description: MCP Client Credentials
User Group: Readers
Click Save.
Note
You can access your newly generated credentials on the Virtana Platform API page to copy Client ID and Secret.
Prerequisites
Ensure you have the following requirements:
Virtana account with API access enabled.
You must have the client credentials, such as client ID and secret.
Admin privileges to install software on your system.
Installation and Setup
The setup process involves installing the Goose client, configuring your preferred LLM provider (such as OpenAI), and adding the Virtana MCP extension. After completing the setup, we recommend running a test chat to verify the integration.
Note
Note that the Goose client and OpenAI LLM provider are optional components; users can choose any MCP-compatible client and LLM provider that suits their environment.
Install Goose Client
To install the Goose Client, perform the following steps:
Download Goose Client v1.12.0 from: Goose Client.
The Goose Client version 1.12.0 is recommended for the best compatibility with Virtana's Alerts MCP server and can be installed on different operating systems
Extract the archive if required, then run the installer executable.
Select OTHER Providers, and then choose OpenAI as the provider type (LLM backend).
Configure OpenAI Provider
Note
Monitor your LLM token/cost usage during MCP interactions. Some prompts generate multiple tool calls and back-and-forth requests, which can result in higher-than-expected token consumption. Track usage through your LLM provider's dashboard.
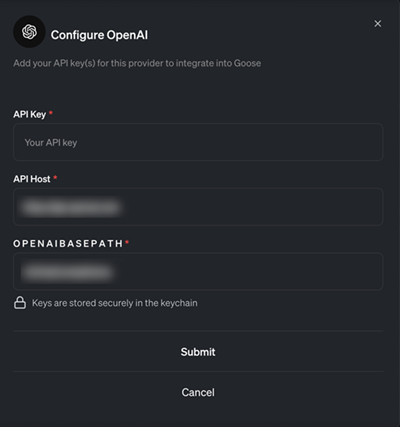
To configure the OpenAI provider in Goose, perform the following steps:
Launch Goose.
In the setup or configuration screen, go to the Providers section.
Enter your OpenAI API Key in the API key field.
If you do not have an API key, contact your Virtana administrator or Virtana support to request one.
Save the configuration to complete the provider setup.
Add the Virtana MCP Extension
To add the Virtana MCP extension, perform the following steps:
In the Goose client, open the left navigation and select Extensions.
Click Add Custom Extension.
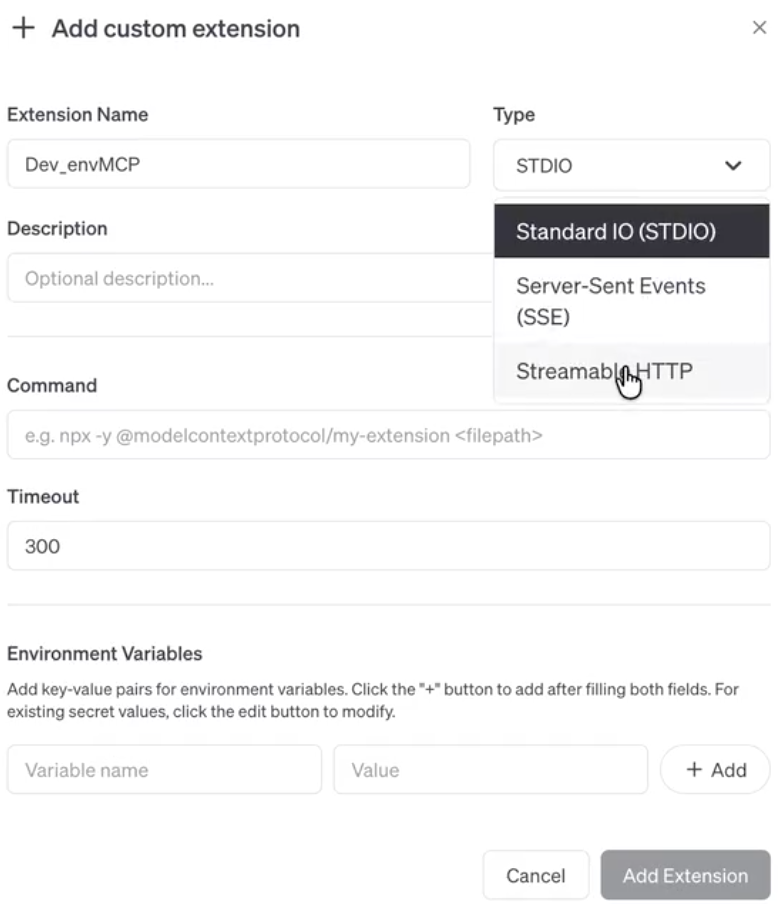
Enter the extension name
Enter the Type as Streamable HTTP.
Note
When you select HTTP as the type, the Endpoint options become available.
Enter Endpoint / MCP URL as :
https://app.cloud.virtana.com/mcp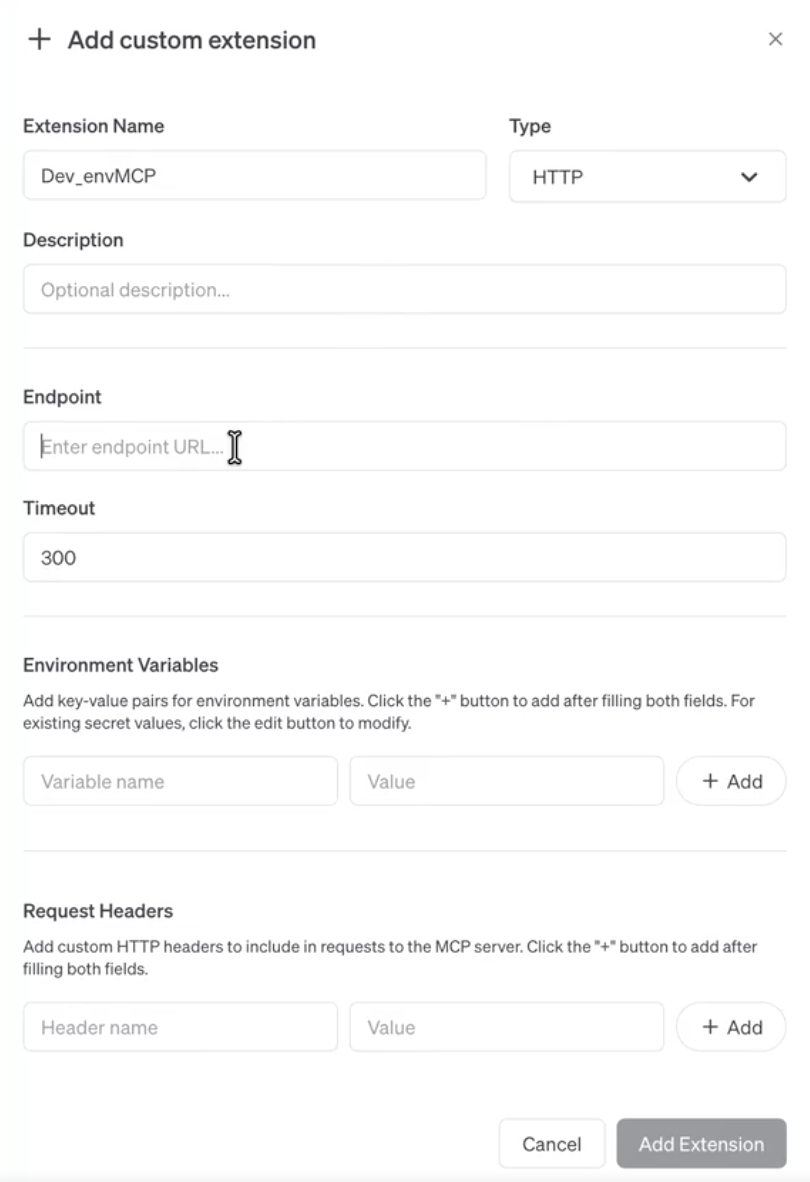
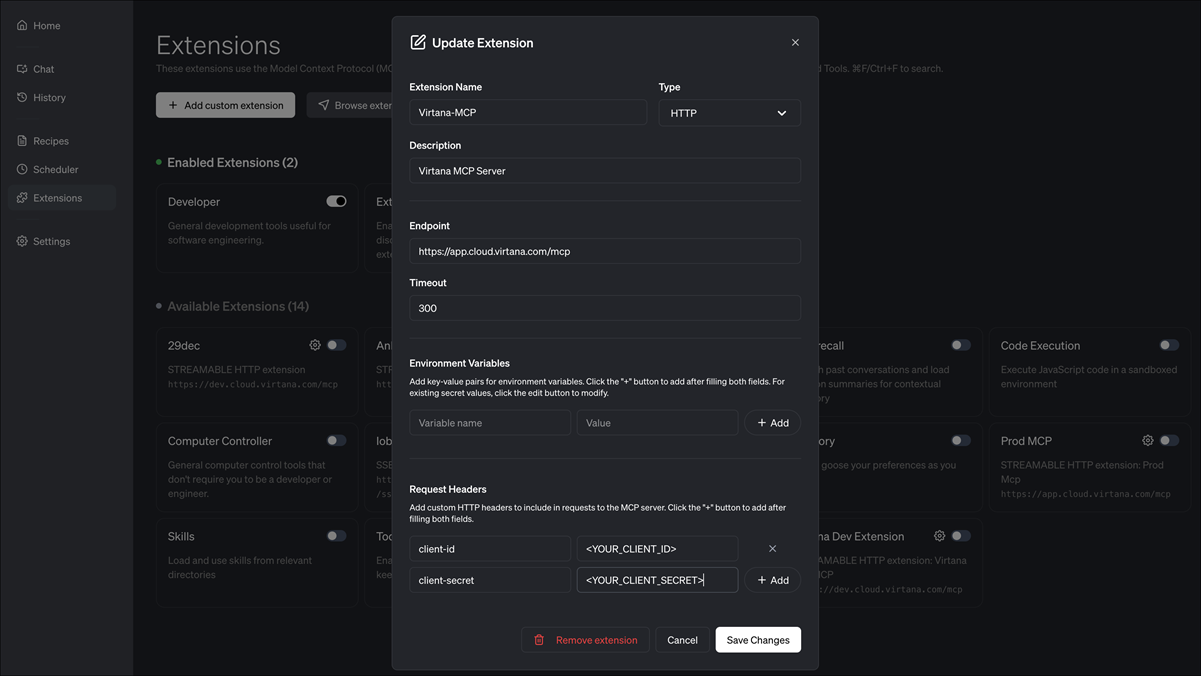
Navigate to Request Headers and add the following header:
client-id: <YOUR_CLIENT_ID>
client-secret: <YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET>
To generate client-id and client-secret, see Generate OAuth credentials for MCP client.
Optionally, give the extension a meaningful name, such as Virtana Alerts MCP, so users can recognize it easily.
Click Add Extension or Save to keep the configuration.
When successfully activated, you will see all enabled extensions.
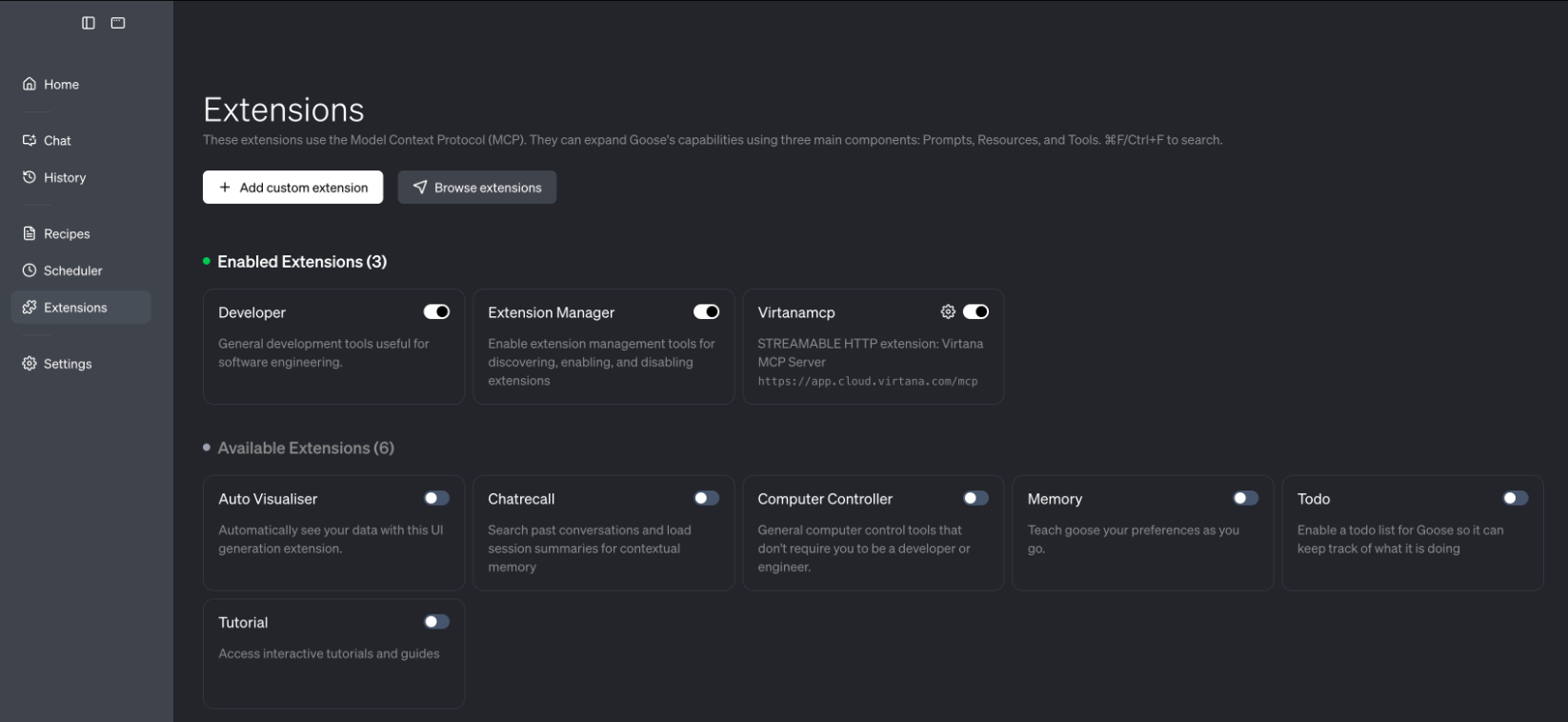
When this configuration is complete, Goose treats the Virtana Alerts MCP server as an extension that exposes tools such as alert query, alert summarization, or other APIs implemented by the Virtana Alerts service.
Start Testing in Chat
To start testing the integration in chat, perform the following steps:
Navigate to the Chat section in Goose.
Make sure the Virtana Alerts MCP extension is enabled for the current session, alongside the OpenAI provider.
Ask alert-related questions, such as:
“Summarize the alerts in the last 24 hours.”
“Which sources produced the most alerts?”
“What is the issue with this entity?” (for a specific entity in Virtana Global View).
Observe how the MCP server responds:
Goose sends your query to the LLM (OpenAI).
The LLM uses the MCP tools exposed by the Virtana Alerts server to fetch real-time data.
The response is returned to the chat with contextual information derived from Virtana’s alert APIs.
Monitoring LLM Token Usage and Costs
Goose provides a built-in indicator to help you monitor LLM token consumption and approximate costs per conversation. At the bottom of the Goose window, you can hover over the token/cost icon to see a breakdown of:
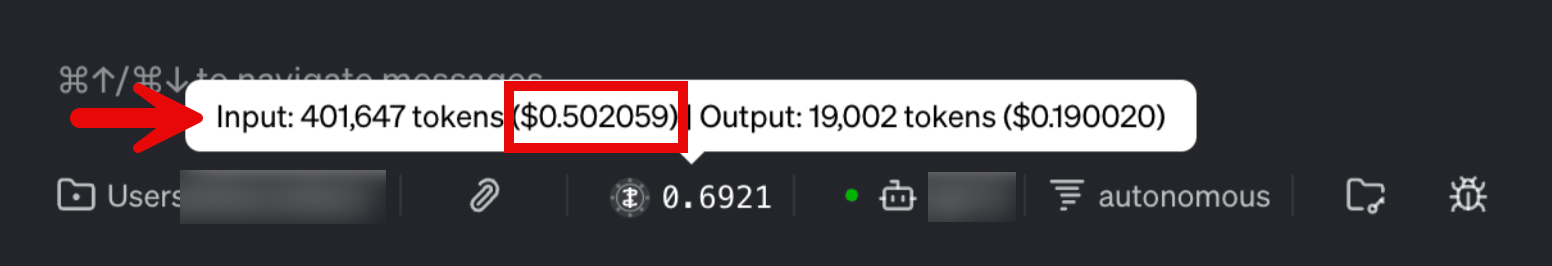
Input tokens and cost
Output tokens and cost
Use this view to regularly check how many tokens your current chat or recipe run is using and to identify prompts that drive unusually high usage.
Note
Keep in mind that Virtana is not responsible if LLM/MCP client tokens are mishandled or if you experience sudden spikes in costs. It is your responsibility to monitor token usage at the session level through their LLM provider dashboards.