Actions
Introduction
Actions are an integral part of the monitoring ecosystem, where problems and issues are addressed and resolved.
The Virtana Wisdom supports the full lifecycle management of action configurations, including Create, Read, Update, and Delete (CRUD) operations. Each operation includes specific steps that interact with user interface elements.
Create an Action Configuration
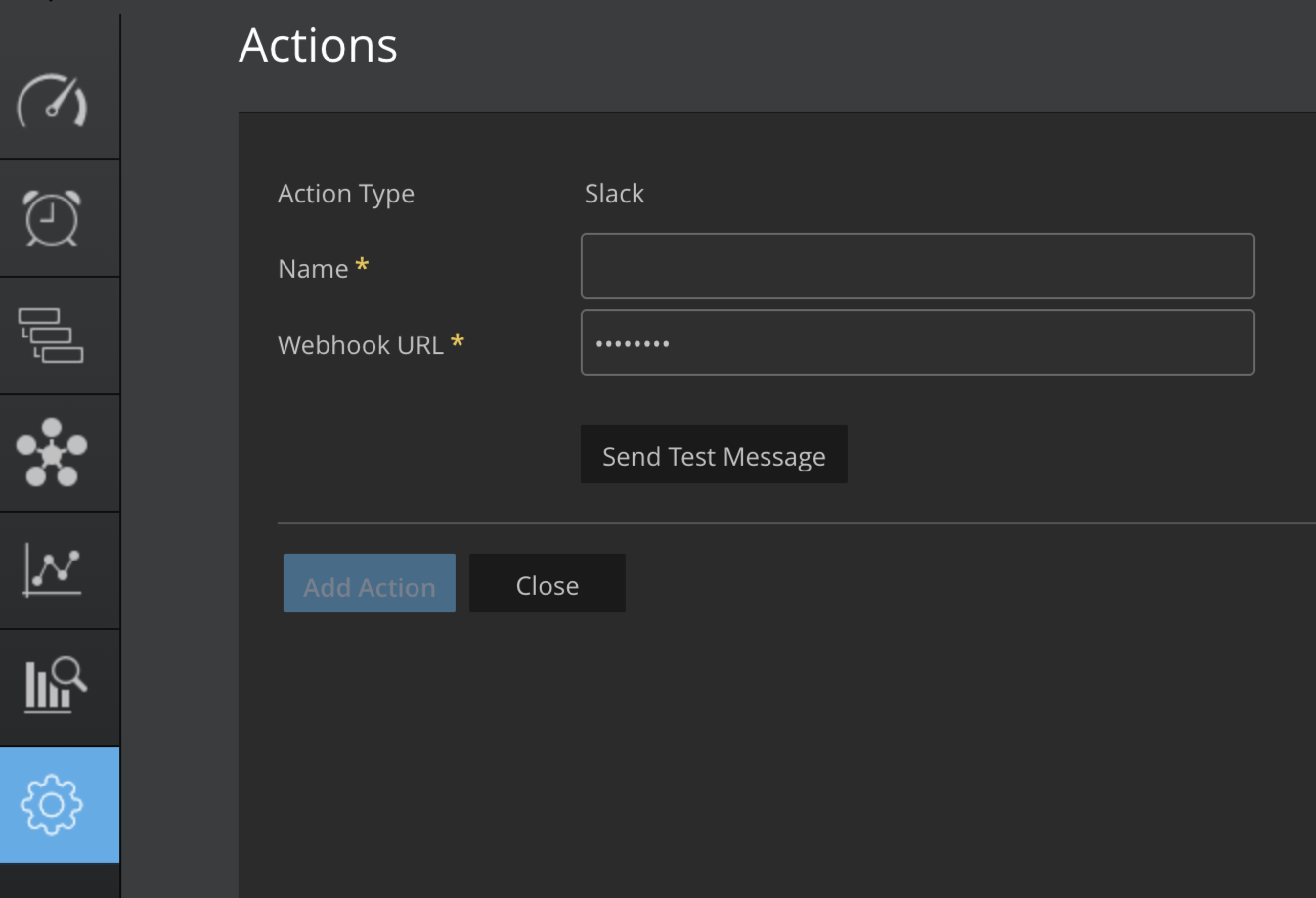
Navigate to Settings > Actions Configuration.
Click on the "Add Action" button. Select the action type from the drop-down menu.
You can select actions such as Slack, MatterMost, Teams, Https, and WebEx
Enter the "Name" in the Name input field.
Enter the "Webhook URL" in the Webhook URL input field.
To test if the webhook URL is correct, click on Send Message.
Click Add Action to save.
Update Action Configuration
Locate an existing action configuration in the list.
Click the "Action Name" in the row go to the edit configuration.
Update the necessary fields (e.g., Name, Webhook URL).
Click the "Save" button.
Delete Action Configuration
Locate an existing action configuration in the list.
Click the "Delete" icon next to the configuration.
In the confirmation dialog, click "OK".
List Action Configurations
Navigate to Configurations List:
Click on Settings > Actions menu item
A list of all available action configurations is displayed.
Search Action Configuration by Name
Click on Settings > Actions menu.
Locate the search bar or search input field at the top of the configurations list page.
Enter the name (or part of the name) of the action configuration you want to search for.
Click the "Search" button.
The list of action configurations remains filtered based on the search query until the search input is cleared or a new search is performed.
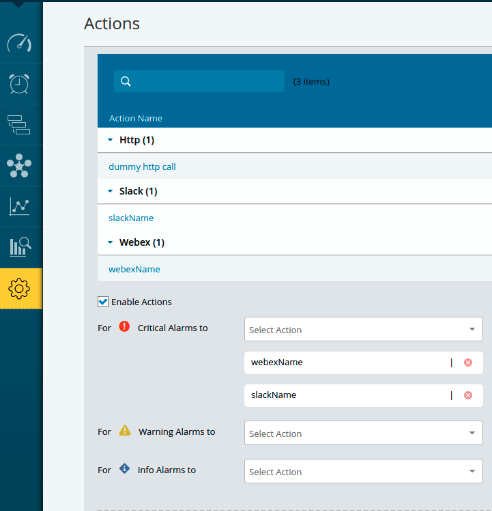
Default Action Policy
For each category of alarms (Info, Warning, and Critical), select the appropriate actions to be triggered. These actions can include notifications, alerts, or any predefined responses based on the severity of the alarm. Action configuration supports setting multiple actions, allowing you to configure various action types for both rules and actions settings.
Alarm Rules
To create Alarm rule:
Navigate to Alarms >Rules >Create New Rule.
To set up a new rule, choose the option for multiple action types as the target for notifications
Based on the selections made in the rule configuration screen, the chosen multiple action types will be triggered, and notifications will be sent using the action service.
For existing rules, you can edit and modify the action type selections as needed.
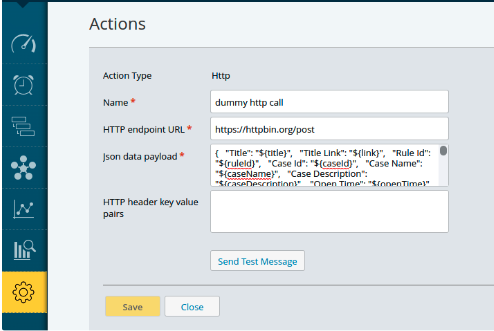
Create an HTTP Configuration
Here are the steps to use the newly added HTTP action type.
Navigate to Settings > Administration >Action menu.
To create a new action, select Add Action from the drop-down menu and choose the HTTP type.
Provide the Name, HTTP endpoint URL, JSON data payload. (Refer to the sample)
Add the HTTP header key value pair. (Refer to the sample)
Note
Following is the sample JSON and the Header key values to enter.
In a document, we must provide a json sample format as an input. Refer to the following sample json for more details:
{
"title": "${title}",
"titleLink": "${link}",
"ruleId": "${ruleId}",
"caseId": "${caseId}",
"caseName": "${caseName}",
"caseDescription": "${caseDescription}",
"openTime": "${openTime}",
"entityName": "${entityName}",
"entityType": "${entityType}",
"ruleName": "${ruleName}",
"ruleType": "${ruleType}"<#if condition?has_content>,
"ruleCondition": "${condition}"</#if>,
"thresholdValues": [
<#list thresholdValues as value>
{
"gaugeName": "${value.gaugeName}",
"threshold": <#if (isPropertyTemplate?? && isPropertyTemplate) && (value.exceededValueString?? && value.exceededValueString?has_content)>
"${value.exceededValueString}"
<#else>
"Threshold: ${value.threshold}, Exceeded Value: ${value.exceededValue}"
</#if>
}<#if value_has_next>,</#if>
</#list>
],
"sourceUuid": "${sourceUuid}",
"severity": "${severity}"
}Description
${title}: The title of the alert.
${link}: A hyperlink (URL) that redirects to a detailed view or monitoring dashboard for this alert/case.
${ruleId}: The unique identifier of the rule that triggered alert.
${caseId}: The unique identifier of the case/incident created.
${caseName}: A human-readable name of the case.
${caseDescription}: A detailed description of the case/incident.
${openTime}: The openTime is date and time (UTC) at which an action was initiated. (yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss, e.g., 2025-07-29 16:55:00 UTC).
${entityName}: The name of the entity (server, application, database, etc.) for which the alert was generated. (e.g., qe-appdisc-01.lab.vi.local)
${entityType}: The name of the entity type selected from the UI (e.g., ESXHost). This represents the class or category of the monitored entity.
${ruleName}: The descriptive name of the monitoring rule responsible for generating the alert.
${ruleType}: Defines the category of the rule being used. Common rule types include:
Single Metric Rule: Monitors a single metric against a fixed threshold or range. The rule is triggered when the metric crosses the specified boundary.
Single Metric Dynamic Rule: Similar to a Single Metric Rule, but uses a dynamic, adaptive threshold based on historical data or behavior patterns.
Property Rule: Evaluates the attributes or properties of an entity, rather than metrics, to determine if conditions are met.
If the rule type is not explicitly listed, it may be one selected from a predefined rule template available in the UI.
"${condition}: The actual condition expression that triggered the rule. This belong to property rule.
${value.threshold}: A list of threshold comparisons and the metric values that exceeded them.
${sourceUuid}: The system’s unique identifier of the source that reported the event/metric.
${severity}: This is the rule severity possible value - info, warning, or critical, based on the selected rule.
${value.gaugeName}: The name of the metric (gauge) that was evaluated by the rule.
${value.threshold}: The threshold value defined in the rule that the metric was compared against.
${value.exceededValue}: The actual value reported by the metric that crossed the threshold.
Header key values to enter:
{ "Accept": "application/json"}Here is the snippet
ServiceNow event notification via Actions
The ServiceNow event notification can be received via Actions in the Virtana environment. To integrate this, use the following sample JSON data playload:
{
"records": [
{
"source": "Virtana",
"event_class": "${sourceUuid}",
"resource": "${entityName}",
"node": "${sourceUuid}",
"metric_name": "${caseName}",
"type": "${entityType}",
"severity": "1",
"description": "${caseDescription}",
"additional_info": "${link}"
}
]
}
Enter the following in the Header key value pair section:
{
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Basic <auth token>"
}
Replace the <auth token> with the actual basic auth token. A token can be generated with the command below.
Bash shell command for Linux or Mac users
echo $(echo -n '<username>:<password>' | base64)
Where <username> and <password> are the servicenow credentials.
Powershell command for Windows users -
[Convert]::ToBase64String([Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetBytes("<username>:<password>"))
Using browser and a third party site example: Generate http Basic Auth Header.
The details of how basic access authentication token is generated can be found on this Wikipedia page: Basic access authentication .
Slack App Webhook Url
You can integrate Slack with Virtana’s platform using Slack's Incoming Webhooks feature. This enables external services to send automated messages directly into specified Slack channels. Follow the steps below to generate and use a Slack Webhook URL.
Note
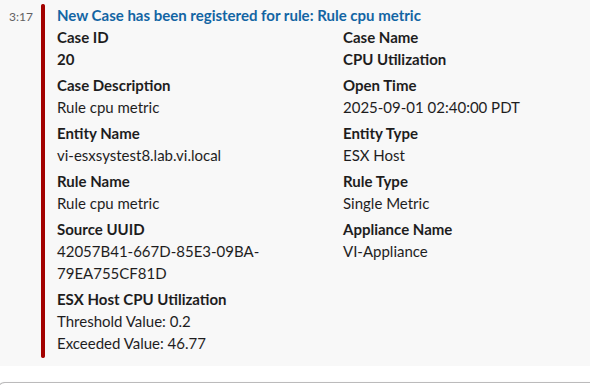
All the details you see in the screenshot (Case ID, Rule Type, Description, Severity, etc.) will appear the same in Slack, Teams, and Webex notifications.
Visit Slack API https://api.slack.com/apps.
Click Create an App.
Select From scratch.
Enter an App Name and select the Slack Workspace for installation.
Click Create App.
In the app configuration page, go to the left-hand navigation pane.
Click Incoming Webhooks.
Toggle the option to Activate Incoming Webhooks.
Scroll down to Webhook URLs for Your Workspace, click Add New Webhook to Workspace.
Select the Slack Channel where you want messages to be posted.
Click Allow to grant permission.
Copy the generated Webhook URL displayed under Webhook URLs for Your Workspace.
After authorizing, you'll be redirected back to the app's settings.
Copy the webhook URL will be displayed under "Webhook URLs for Your Workspace.
Use the webhook url in the add action in the UI.
Microsoft Teams App Webhook Url
Go to the Microsoft Teams app or the web version.
Choose the Your Teams where you want to send messages using the webhook.
Click on the "More options" (three dots) next to the channel name.
Click on Apps menu.
Click on Incoming Webhook and Add another team button.
Select channel name and set up a "Connectors".
To set up an Incoming Webhook, provide a name and select Create.
Click on create button.
After creation, the Webhook URL will be displayed. Copy this URL as you'll need it to send messages to the Teams channel.
Use the webhook url in the add action in the UI.
Webex Chat App Webhook Url
Open your browser and go to Webex Developer Portal.
Sign in to Your Webex Account.
From the list of available options, choose Webhook as the app type.
Selecting Webhook allows you to configure the app to receive data from Webex when specific events occur.
Configure the Webhook:
Name: Give your webhook a name (e.g., Incoming Webhook for Space).
Target URL: Enter the endpoint where Webex should send JSON notifications.
Resource: Select what to monitor (e.g., messages).
Event: Choose the event type (e.g., created for new messages).
Filter: Add roomId to specify the Webex space.
Secret (optional): Set a secret key to verify incoming webhook data.
Click Create to finalize and create your webhook.